How Much Protein Do You Need: Building Muscle

Have you ever wondered how much protein is needed to build muscle? Contrary to popular belief, you don't need mountains of chicken breast!
I'm Dakota, a certified Exercise Physiologist and Strength and Nutrition coach passionate about helping people achieve their health and fitness goals. Today, I'm excited to give you a research-based answer to how much protein you need to optimize muscle building!
Protein is the building block of our muscles. So, when you work out (lift weights or run!), you create little tears in your muscles. Protein repairs and rebuilds those tears, which leads to muscle growth and strength.
Understanding Protein Needs
When understanding your protein needs, looking at your Lean Body Mass (LBM) is important. This includes your muscles, organs, bones, and other tissues, except for fat. LBM is a more accurate measure for protein requirements because the amount of protein you need depends on your lean tissues' repair and renewal needs.
To calculate your lean body mass, multiply your total body weight by your percentage of body fat to obtain the total pounds of body fat. Afterward, subtract the total pounds of body fat from your total body weight to determine your lean body mass.
Body Weight x %Body Fat = Body Fat in Pounds
Body Weight - Body Fat in Pounds = Lean Body Mass
You need protein to promote a positive nitrogen balance to maintain a healthy body. Nitrogen balance is simply the balance between the amount of protein you consume and the amount of protein your body breaks down.
If you're looking to build muscle, you need to be in a positive nitrogen balance, meaning you should consume more protein than your body breaks down during exercise.
By maintaining a positive nitrogen balance, your body encourages muscle protein synthesis. This is how your body uses amino acids, the tiny organic components of protein, to build and repair muscle tissue.
Let's get to the point you searched for how much protein you should get daily!
Protein Intake Recommendations
Perhaps you're interested in optimizing your progress towards having more energy and feeling better or building bigger muscles to improve your overall fitness. Whatever your reason, protein requirements fit into two categories (maintaining health or building muscle).
Please feel free to skip ahead to the category that best fits you!
Daily protein needs for a healthy, sedentary adult(s)
In the US, the RDA for protein is 0.8 grams per kilogram or 0.36 grams per pound of total body weight, which was determined using nitrogen balance [3]. However, recent research suggests that this amount is quite low and that the RDA should be increased to 1.0 grams per kilogram or 0.45 grams per pound of total body weight [2].
I also wanted to share some interesting research on the amount of protein required for muscle maintenance or growth after eight weeks [1]. The study involved participants consuming an excess of calories (calorie surplus!) but with different protein ratios in their diets.
Eight weeks of low, normal, or high protein categories:
- Low: 0.8g/kg
- Normal: 1.8g/kg
- High: 3g/kg
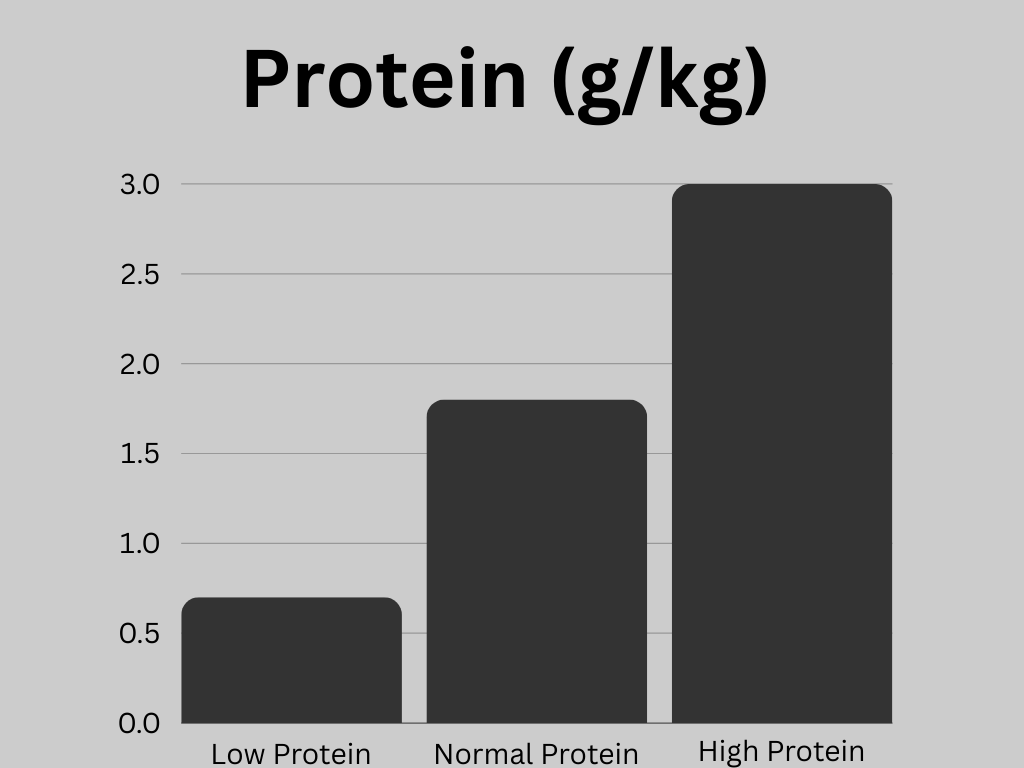
During the eight-week study, eating the RDA for protein (low protein group!) resulted in the loss of lean body mass; the loss was so small it was considered insignificant, and the normal and high protein increased lean body mass.
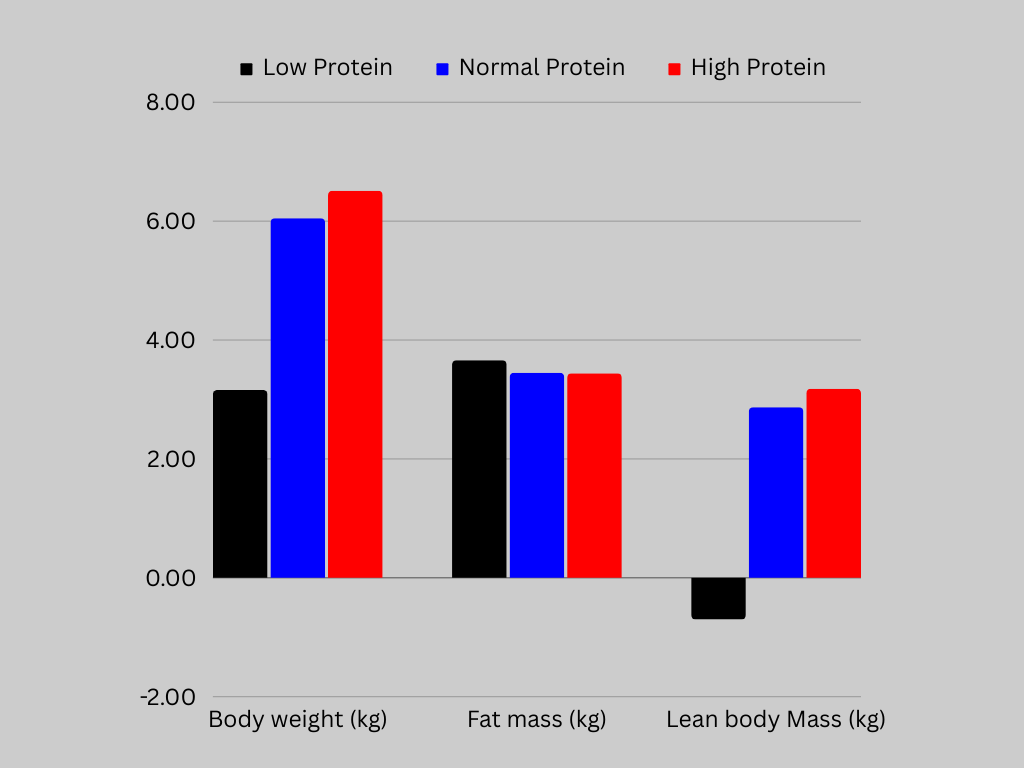
In summary, the RDA for protein (0.8 grams per kilogram) is below the requirements of healthy, sedentary adults, who should consider a protein intake of 1.2-1.8 grams per kilogram or 0.54-0.81 grams per pound of total body weight.
Daily protein needs for muscle gain in adults
If you want to build some serious muscle, you must increase your protein intake beyond the recommended daily amount. But don't worry—I'll help you find what you need! Knowing your lean body mass is also important, as it will help you track progress and determine how much protein your body needs.
To promote muscle growth, it's suggested that you aim for 1.8 grams of protein per kilogram or 0.81 grams per pound of your lean body mass daily. For example, if your lean body mass is 70 kg, you should aim for 126 grams of protein per day (1.8 g/kg x 70 kg).
If you want to maximize muscle protein synthesis, then it's suggested that you consume between 2.2-2.4 grams of protein per kilogram or 1-1.8 grams per pound of your lean body mass. For someone with 70 kg of LBM, the optimal range would be 154-168 grams of protein per day.
There's no known limit to how much protein you can consume daily to optimize muscle gains in healthy individuals. However, going beyond the optimal intake (2.2-2.4 g/kg) is unlikely to provide significant additional benefits and may be more expensive or inconvenient. So, find the sweet spot that works for you and enjoy the gains!
Factors That Influence Your Protein Needs
Whether you are into fitness or a sedentary, healthy adult, there are three key factors you should keep in mind to guarantee that you're getting the right amount of protein for building muscle.
First, our bodies become less efficient at using protein as we age. If you're over 30, you may need to increase your protein intake by around 1.5% per year to achieve the same muscle-building effects.
Secondly, monitoring the number of calories you're consuming is important. If you're in a calorie deficit (i.e., consuming fewer calories than you're burning), your body will start breaking down muscle for energy.
To prevent this, you may need to increase your protein intake by 10-20% (while in a calorie deficit!). For example, if you're already consuming the optimal amount of protein (around 2.2-2.4 g/kg LBM) and are in a calorie deficit, you should aim for 2.42-2.88 g/kg LBM daily.
Finally, if you're a highly active person, such as a marathon, triathlon, or Ironman athlete, you may need to consume an extra 5-10 grams of protein for each hour of exercise to maintain or potentially increase your muscle mass.
For example, if you have a lean body mass of 70 kg, you should aim for around 154-168 grams of protein per day (2.2-2.4 g/kg LBM). However, if you're going for a 3-hour run, you should consume an additional 5-10 grams of protein per hour of exercise, which means your total daily protein intake should be around 169-198 grams.
Conclusion
Your daily protein intake is just the start of caring for your body. Remember that fueling it with the right nutrients is super important to reach your fitness goals.
As a healthy adult, you should aim for 2.2-2.4 g/kg of lean body mass for optimal muscle building. If you're interested in learning more about finding protein sources, building a balanced diet, and getting other fitness tips, consider subscribing.
And hey, how much protein do you think you need to add to your diet? I'd love to hear from you in the comments below!
References
- Bray, G. A., Smith, S. R., de Jonge, L., Xie, H., Rood, J., Martin, C. K., Most, M., Brock, C., Mancuso, S., & Redman, L. M. (2012). Effect of dietary protein content on weight gain, energy expenditure, and body composition during overeating: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA, 307(1), 47–55. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2011.1918
- Elango, R., Humayun, M. A., Ball, R. O., & Pencharz, P. B. (2010). Evidence that protein requirements have been significantly underestimated. Current opinion in clinical nutrition and metabolic care, 13(1), 52–57. https://doi.org/10.1097/MCO.0b013e328332f9b7
- Dietary Reference Intakes for Energy, Carbohydrate, Fiber, Fat, Fatty Acids, Cholesterol, Protein, and Amino Acids (2005)
National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine. 2005. Dietary Reference Intakes for Energy, Carbohydrate, Fiber, Fat, Fatty Acids, Cholesterol, Protein, and Amino Acids. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press. https://doi.org/10.17226/10490.